Design Technology
There is an ambitious curriculum set for Design Technology, supporting teachers to implement it through high-quality lessons and checking that everything is helping children to know more, remember more and do more.
If you would like more information in addition to that published on this page, please contact your class teacher.
Purpose of Study
Design and technology is an inspiring, rigorous and practical subject. Using creativity and imagination, pupils design and make products that solve real and relevant problems within a variety of contexts, considering their own and others’ needs, wants and values. They acquire a broad range of subject knowledge and draw on disciplines such as mathematics, science, engineering, computing and art. Pupils learn how to take risks, becoming resourceful, innovative, enterprising and capable citizens. Through the evaluation of past and present design and technology, they develop a critical understanding of its impact on daily life and the wider world. High-quality design and technology education makes an essential contribution to the creativity, culture, wealth and well-being of the nation.
Aims
The National Curriculum - DT key stages 1 to 2
- Develop the creative, technical and practical expertise needed to perform everyday tasks confidently and to participate successfully in an increasingly technological world
- build and apply a repertoire of knowledge, understanding and skills in order to design and make high-quality prototypes and products for a wide range of users
- critique, evaluate and test their ideas and products and the work of others
- understand and apply the principles of nutrition and learn how to cook.
Oakfield's Approach
Inspirational People
At our school, we believe in using the power of inspiration to help shape the thinking and curriculum design of our students. That's why we have taken inspiration from successful and influential people who have made a significant impact in their respective fields. By studying their stories, we aim to inspire our pupils to aim high and achieve their own goals. We have carefully curated a list of inspirational figures, including scientists, artists, entrepreneurs, and activists, to name a few. We have analysed what made them successful and incorporated their values, principles, and strategies into our curriculum design to provide our students with the tools they need to succeed. By doing so, we hope to empower our students to dream big and achieve greatness.

Intent
We are setting out to help our pupils be ...
-
Safe - Learn to use tools safely for everyday life, including computers to design products. Children learn how to be healthy.
-
Creative - Children love to design and make their own creations.
-
Resilient - Children are resilient and enjoy creating even when things do not go right the first time.
-
Cultured - Children build a repertoire of knowledge, understanding and skills in order to design and make products for a wide range of users.

Implementation
We will do this by ensuring ...
-
Children have a broad and balanced curriculum - Tool skills and nutrition are taught progressively.
-
Children have a broad and balanced curriculum - The process of designing, making and evaluating is embedded in the curriculum.
-
Giving children time - Children have time to explore materials and try out different ideas.
-
Children have a broad and balanced curriculum - There are planned, progressive and purposeful opportunities to design and make in the curriculum.

Impact
We will have made a difference when ...
-
Children apply what they know - Children can use tools practically and make informed, healthy choices in life.
-
Children are inventors - Children can enjoy the process and create things successfully.
-
Children can create purposefully - Children are reflective and consciously evaluate what they do to improve.
-
Children can show what they know - Children can make models with success and develop them to improve.
Threshold Concepts
These are our big takeaways called ‘threshold concepts’ - an overview of what we want pupils to know. They are the same for every year group and help us to ensure we build learning on the same ideas, that way we help children to be able to remember more meaningful connections rather than remembering isolated facts.
-
Everyday products - Everyday products are objects that are used routinely at home and school.
-
Staying Safe - It is important to stay safe when working with tools. Products have to be safe for others to use.
-
Electricity - Electricity is a form of energy, it can be used in a model and controlled using a switch.
-
Mechanisms - Mechanisms help to make things move.
-
Generation of ideas - Before making, it is important to know what you want to achieve.
-
Use of ICT - Computer-aided design (CAD) is when computers are used to help design products.
-
Structures - Different materials can be used to make structures stronger.
-
Investigation - Great designers try to find the best tool for the job.
-
Evaluation - To make improvements, it is important to find out what has worked well and what could be better.
-
Materials for Purposes - Different materials are suitable for different purposes, depending on their properties.
-
Cooking - We use skills such as measuring and follow instructions called recipes to make sweet and savoury dishes.
-
Nutrition - There are different types of food that our body needs to stay healthy.
-
Origins of Food - Food can be grown or can come from animals. We often eat food that comes from around the world.
-
Compare & Contrast - Designers often look at what is the same and what is different between products.
-
Significant People - Because of the work of many important designers, the way we live our lives has changed.

Progression on a Page ...
Here is an overview of what we expect children to be taught, know and do by the end of each year group.

In Year R ... Children will be taught to ...
-
Name and explore a range of everyday products and begin to talk about how they are used.
-
Follow rules and instructions to keep safe.
-
Identify products that use electricity to make them work.
-
Explore, build and play with a range of resources and construction kits with wheels and axles.
-
Create collaboratively, share ideas and use a variety of resources to make products inspired by existing products, stories or their own ideas, interests or experiences.
-
Use digital devices to take digital images or recordings of their creations to share with others.
-
Construct simple structures and models using a range of materials.
-
Choose and explore appropriate tools for simple practical tasks.
-
Adapt and refine their work as they are constructing and making.
-
Recognise that it is possible to change and alter their designs and ideas as they are making them.
-
Select appropriate materials when constructing and making.
-
Follow instructions, including simple recipes, that include measures and ingredients.
-
Suggest healthy ingredients that can be used to make simple snacks.
-
Begin to identify the origins of some foods.

Year 1
-
Children should know that everyday products are objects that are used routinely at home and school.
-
They will understand that rules are made to keep people safe from danger.
-
Electricity is a form of energy.
-
An axle is a rod or spindle that passes through the centre of a wheel to connect two wheels.
-
Design criteria are the explicit goals that a project must achieve.
-
They will understand that a strength is a good quality of a piece of work. A weakness is an area that could be improved.
Year 2
-
Children should know that products can be improved in different ways.
-
They will know that hygiene rules include washing hands before handling food, cleaning surfaces, tying long hair back, storing food appropriately and wiping up spills.
-
They will learn that a series circuit is made up of an energy source.
-
A mechanism is a device that takes one type of motion or force and produces a different one.
-
Ideas can be communicated in a variety of ways, and finished products can be compared with design criteria to see how closely they match. Improvements can then be planned.
Year 3
-
Children will learn that particular products have been designed for specific tasks.
-
They will know that safety rules must also be followed when using electricity.
-
An electric circuit can be used in a model.
-
Levers consist of a rigid bar that rotates around a fixed point, called a fulcrum.
-
They will understand that design criteria are the exact goals a project must achieve to be successful.
-
They will learn that asking questions can help others to evaluate their products.
-
Children will learn that design features are the aspects of a product's design that the designer would like to emphasise.
-
They will learn to take appropriate safety precautions, such as wearing goggles and gloves, working in a well-ventilated room, wiping up spills and tying back long hair.
-
They will know that components can be added to circuits to achieve a particular goal.
-
Mechanisms can be used to add functionality to a model.
-
Annotated sketches and exploded diagrams show specific parts of a design.
-
Evaluation can be done by considering whether the product does what it was designed to do, whether it has an attractive appearance, what changes were made during the making process and why the changes were made.

Year 5
-
Children will learn that culture affects the design of some products.
-
They will know that safety features are often incorporated into products that might cause harm.
-
Electrical circuits can be controlled by a simple on/off switch, Pneumatic systems use energy that is stored in compressed air to do work.
-
A pattern piece is a drawing or shape used to guide how to make something.
-
They will understand that testing a product against the design criteria will highlight anything that needs improvement or redesign.
Year 6
-
Children will learn that people's lives have been improved in countless ways due to new inventions and designs.
-
They will understand that the safety of the user has to be taken into account when designing a new product.
-
Computer programs can control electrical circuits. Mechanical systems can include sliders, levers, linkages, gears, pulleys and cams. Design criteria should cover the intended use of the product, age range targeted and final appearance.
-
Design is an iterative process, meaning alterations and improvements are made continually throughout the manufacturing process.
-
They will know that evaluating a product while it's being manufactured, and explaining these evaluations to others, can help to refine it.
Units of Learning ...

Year 1 - Autumn
Shade & Shelter
This project teaches children about the purpose of shelters and their materials. They name and describe shelters and design and make shelter prototypes. Children then design and build a play den as a group and evaluate their completed product.

Year 1 - Spring
Taxi
This project teaches children about wheels, axles and chassis and how they work together to make a vehicle move.

Year 1 - Summer
Chop, Slice & Mash
This project teaches children about sources of food and the preparatory skills of peeling, tearing, slicing, chopping, mashing and grating. They use this knowledge and techniques to design and make a supermarket sandwich according to specific design criteria.

Year 2 - Autumn
Remarkable Recipes
This project teaches children about sources of food and tools used for food preparation. They also discover why some foods are cooked and learn to read a simple recipe. The children choose and make a new school meal that fulfils specific design criteria.

Year 2 - Spring
Beach Hut
This project teaches children about making and strengthening structures, including different ways of joining materials.

Year 2 - Summer
Push & Pull
This project teaches children about three types of mechanism: sliders, levers and linkages. They make models of each mechanism before designing and making a greetings card with a moving part.

Year 3 - Autumn
Cook Well, Eat Well
This project teaches children about food groups and the Eatwell guide. They learn about methods of cooking and explore these by cooking potatoes and ratatouille. The children choose and make a taco filling according to specific design criteria.

Year 3 - Spring
Making It Move
This project teaches children about cam mechanisms. They experiment with different shaped cams before designing, making and evaluating a child's automaton toy.
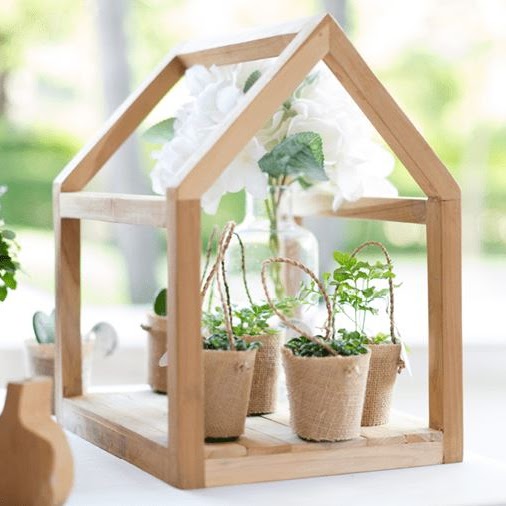

Year 3 - Summer
Greenhouse
This project teaches children about the purpose, structure and design features of greenhouses, and compares the work of two significant greenhouse designers. They learn techniques to strengthen structures and use tools safely. They use their learning to design and construct a mini greenhouse.

Year 4 - Autumn
Fresh Food, Good Food
This project teaches children about food decay and preservation. They discover key inventions in food preservation and packaging, then make examples. The children prepare, package and evaluate a healthy snack.

Year 4 - Spring
Functional & Fancy Fabrics
This project teaches children about home furnishings and the significant designer William Morris. They learn techniques for decorating fabric, including block printing, hemming and embroidery and use them to design and make a fabric sample.

Year 4 - Summer
Tomb Builders
This project teaches children about simple machines, including wheels, axles, inclined planes, pulleys and levers, exploring how they helped ancient builders to lift and move heavy loads.

Year 5 - Autumn
Moving Mechanisms
This project teaches children about pneumatic systems. They experiment with pneumatics before designing, making and evaluating a pneumatic machine that performs a useful function.

Year 5 - Spring
Eat The Seasons
This project teaches children about the meaning and benefits of seasonal eating, including food preparation and cooking techniques.

Year 5 - Summer
Architecture
This project teaches children about how architectural style and technology has developed over time and then use this knowledge to design a building with specific features.

Year 6 - Autumn
Make Do & Mend
This project teaches children a range of simple sewing stitches, including ways of recycling and repurposing old clothes and materials.

Year 6 - Spring
Engineer
This project teaches children about remarkable engineers and significant bridges, learning to identify features, such as beams, arches and trusses. They complete a bridge-building engineering challenge to create a bridge prototype.

Year 6 - Summer
Food for Life
This project teaches children about processed food and healthy food choices. They make bread and pasta sauces and learn about the benefits of whole foods. They plan and make meals as part of a healthy daily menu, and evaluate their completed products.






